
Topographic descriptions and the relationships between the various air cavities and paranasal sinuses have been visualized using computed tomography and cadaver sections images. The purpose of this chapter is to present an anatomical reference guide of the paranasal sinuses in domestic animals, including large and small ruminants (cattle, buffalo, sheep, and goats), camels, canines (dog) and equines (horse and donkey), appropriate for use by anatomists, radiologists, clinicians, and veterinary students. Thus, each sinus is lined by respiratory epithelium and has direct or indirect communication to the nasal cavity. In some cases, extra bone pieces within the suture are called sutural or wormian bones.Paranasal sinuses are paired cavities within the skull, which develop by evagination into the spongy bone between the external and internal plates of the cranial and facial bones. The hyoid bone has a horse-shoe structure at the base of the tongue. The skull bones are joined by sutures (except the mandible) formed by ossification, with perforating fibres promoting flexibility These include fourteen facial skeleton bones and eight cranial bones In general, the human skull has 22 bones. The total number of bones in the human skull has 29, including the hyoid bone and the inner ear bone. Mainly there are four types of bones, they are The human skull consists of various types of bones. It also includes the anterior part of the skeleton and is a by-product of several sensory organs such as the ears, nose, mouth, and eyes And these two regions are in the form of the viscerocranium and the neurocranium.
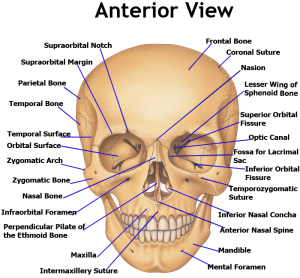
The skull is mainly constituted of two parts the mandible and the cranium.
It supports the networks of the facial expression and acts as a protective cover to the cavity The skull is a vertebrate consisting of bones that give the head structure. The total number of bones found in the human skull is A.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
